Most teams do not struggle to adopt cloud. They struggle to manage what happens after adoption: too many vendor portals, too many billing models, and too little clarity on who owns what. Flexera reports that multi-cloud usage rose to 89% (Flexera) in the 2024 State of the Cloud survey. When your services, policies, and invoices are spread across multiple providers, even small mistakes turn into recurring costs, security gaps, and slow delivery.
That is where cloud brokerage software helps. A cloud broker platform sits between you and cloud providers to bring service discovery, provisioning, governance, and billing into one workflow.
For MSPs, resellers, and distributors, it becomes the operational layer behind a cloud marketplace. For enterprises, it becomes the control layer that ties cloud usage to budgets, access policies, and accountability.
Key Takeaways
- Cloud brokerage software turns multi-cloud services into a governed catalog and process.
- A cloud broker platform connects buying, provisioning, and billing so spend matches real usage.
- For MSPs, brokerage supports packaged offers, renewals, and partner-led selling.
- For enterprises, brokerage supports consistent policy, reporting, and chargeback across clouds.
- The best platforms combine provider integrations, workflow control, and billing depth.
- Start with a small catalog, then expand after provisioning and billing are linked.
What does Cloud Brokerage Software mean in Real Terms?
Cloud brokerage software is a platform that helps you find, buy, provision, manage, and bill cloud services from multiple providers through a unified layer.
You can think of it as a digital middle layer that turns a fragmented multi-cloud environment into a repeatable service workflow.
You will see three common labels used in the market:
| Term | How it is used | What it usually includes |
| Cloud broker platform | The software category | Catalog + provisioning + governance |
| Cloud service brokerage | The operating model | Provider aggregation + service delivery |
| Cloud brokerage software | The functional description | Catalog + workflows + reporting + billing |
In practice, the most useful platforms connect commerce and operations. That connection is what reduces friction for both IT teams and revenue teams.
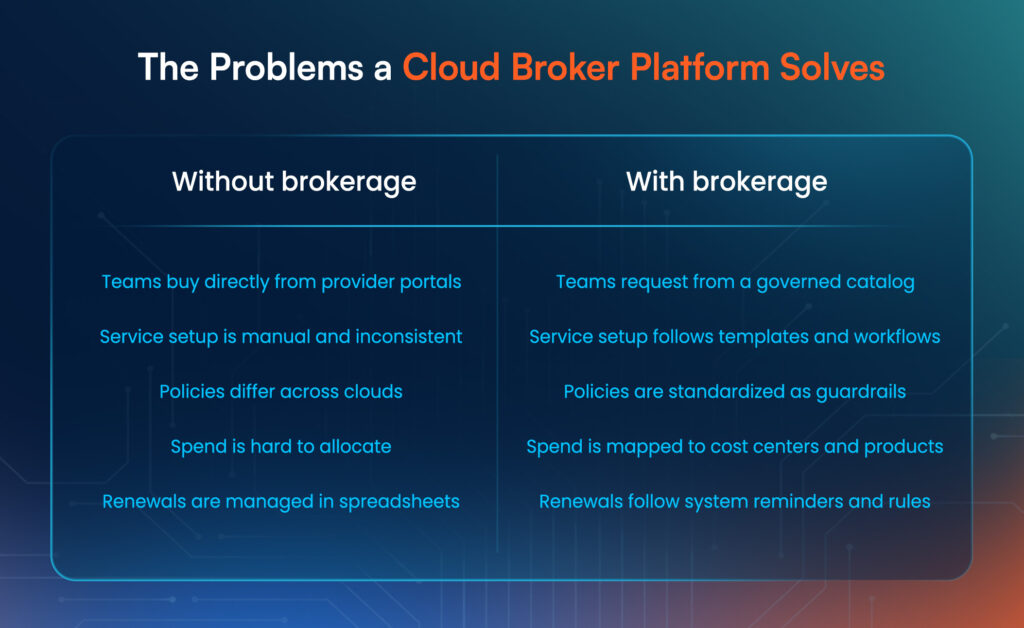
The Problems a Cloud Broker Platform Solves
Multi-cloud creates four common friction points. A broker platform is valuable when it addresses all four, not just one.
1) Procurement becomes inconsistent
Different teams buy services in different ways. Approvals vary. Renewals get scattered. A broker adds standard request flows and catalog governance.
2) Provisioning becomes ticket-heavy
Manual setup increases queue time and configuration drift. A broker uses templates and API-driven provisioning so you can ship consistent builds.
3) Governance becomes fragmented
Each provider has its own policies and dashboards. A broker creates common guardrails, audit trails, and role-based workflows across services.
4) Billing becomes disconnected from usage
Cloud invoices come late, are hard to allocate, and often do not map to business units. Flexera notes that 84% of respondents see managing cloud spend as their top cloud challenge (citation: Flexera).
A broker platform helps by linking service activation to allocation, budgets, and billing logic.
Here is a practical before-and-after view:
How a Cloud Broker Platform works End-to-End?
A cloud broker platform typically follows a service lifecycle that looks like this:
Catalog → Request/Approval → Provisioning → Access & Policy → Monitoring → Billing → Renewal
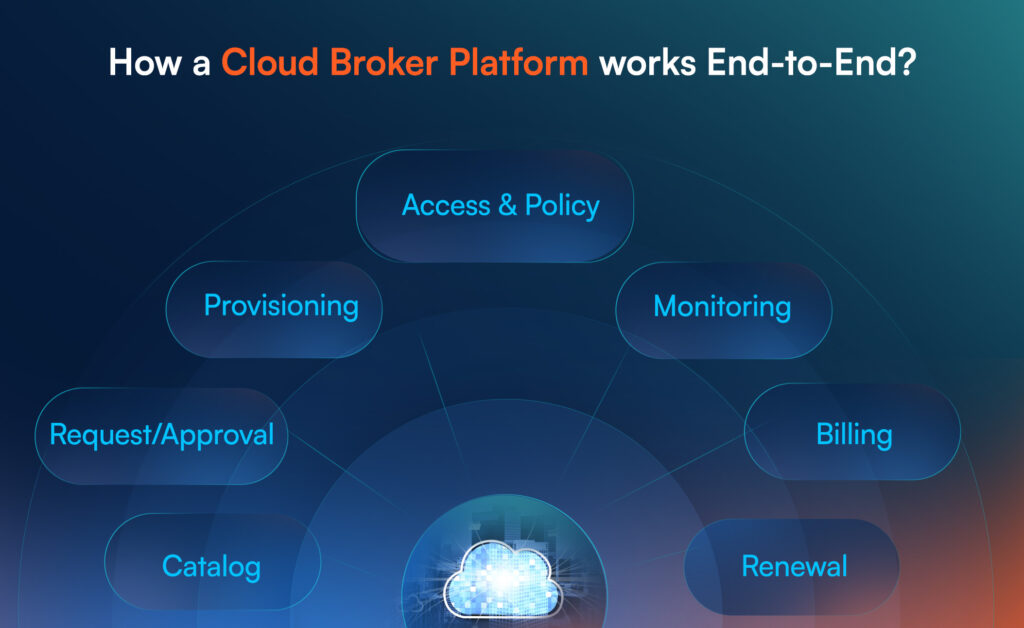
To support that lifecycle, the platform usually includes these building blocks.
Service catalog and bundles
A catalog is the “front door.” It can list:
- Public cloud subscriptions and plans
- SaaS products
- Managed services such as backup, security, monitoring
- Bundles, for example “M365 + endpoint security + backup”
For MSPs, bundles are often where margin and differentiation live.
Orchestration and provisioning
Provisioning connects catalog items to provider APIs and infrastructure templates. This reduces manual tickets and improves consistency across environments.
Identity, access, and audit trails
A broker often becomes a policy layer, so it needs role-based access, approval trails, and clean audit logs. Some buyers also check local compliance expectations, such as log retention.
India’s CERT-In directions require specified entities to retain logs for 180 days (report by: CERT-In), which makes audit readiness a practical evaluation point for platforms used by regulated sectors.
Cost, allocation, and budget control
A broker should not just show spend. It should support allocation rules, budgets, and alerts so teams can act early.
Billing, Invoicing, and Renewals
This is the dividing line between a platform that looks good in a demo and a platform that runs well in production. A platform with billing depth can handle subscription invoices, co-terms, add-ons, and usage-based charges.
Core capabilities that matter most
The AIO patterns for this topic align on five themes: aggregation, orchestration, cost control, governance, and neutrality. Use this feature-to-outcome map to make decisions faster.
| Capability | What it does | What you measure | What to check in the product |
| Aggregation and catalog | Pulls cloud and SaaS offers into one list | Adoption rate, request volume | Provider connectors, catalog controls |
| Provisioning and orchestration | Activates services via APIs and templates | Provisioning time, ticket reduction | Templates, approvals, automation rules |
| Governance and security | Applies guardrails and access controls | Policy compliance, audit readiness | RBAC, audit exports, policy packs |
| Cost visibility and allocation | Maps usage to spend, budgets, owners | Budget variance, unit cost, showback | Tags, allocation rules, budgets, alerts |
| Billing and renewals | Turns activations into invoices and renewals | Billing accuracy, renewal rate | Rating, proration, taxes, co-terms |
Flexera also notes that cloud spend is expected to increase by 28% in the coming year (Flexera)(flexera.com). When spend grows that quickly, the ability to allocate and bill correctly becomes a day-to-day requirement.
Who Uses Cloud Brokerage Software And Why?
Cloud brokerage software shows up wherever teams need one operating layer to buy, manage, and govern cloud services across multiple providers, business units, or reseller channels.
Once AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, and SaaS subscriptions start living in different portals and invoices, teams hit three issues fast: visibility, control, and repeatable delivery. A cloud broker platform solves that by centralizing the service catalog, policies, ordering, billing signals, and reporting under one system of record.
Then continue the section with your user groups (keep it structured like this, and avoid over-bulleting):
- MSPs And IT Service Providers
They use cloud brokerage software to standardize service delivery, reduce manual order handling, and manage multi-tenant customer operations. - Resellers, VARs, And Distributors
They use it to manage catalogs, bundles, pricing rules, and recurring billing across customers and partner tiers. - Enterprises With Multi-Cloud Footprints
They use it to enforce governance, track usage and costs across clouds, and run consistent access and policy controls. - ISVs And SaaS Vendors
They use it to package cloud services with their product, manage subscriptions, and improve customer onboarding workflows. - Telcos And Channel-Led Providers
They use it to run large partner ecosystems with consistent product catalogs, entitlement logic, and billing governance.
Use Cases that Create a Clear ROI
A broker platform becomes easier to justify when it is tied to specific workflows. These are common patterns across global buyers.
| Use case | What the broker changes | Where ROI appears |
| Multi-cloud self-service for internal teams | Standard catalog, approvals, templates | Faster delivery, fewer tickets |
| MSP cloud bundles and managed services | Bundled offers, recurring billing, renewals | Higher ARPU, higher renewal rate |
| Budget control and showback | Allocation rules and budgets | Lower budget overrun, clearer unit costs |
| Compliance workflows | Audit trails and policy guardrails | Faster audits, lower operational risk |
| Contract and renewal management | Co-terms and renewal reminders | Lower churn, less revenue leakage |
Flexera reports that cloud budgets are already exceeding limits by 17% (source: Flexera), which is why spend governance and billing discipline are now part of platform selection, not afterthoughts.
Cloud Broker Platform vs Adjacent Tools
Cloud brokerage software often gets mixed up with other cloud tooling. This comparison helps you avoid buying the wrong category.
| Category | Primary job | What it usually lacks |
| Cloud management platform | Operates infrastructure resources | Commerce and billing workflows |
| ITSM service catalog | Manages internal service requests | Provider provisioning and allocation |
| CASB | Controls data access to cloud apps | Cross-provider service commerce |
| Provider marketplace portal | Sells one provider’s services | Multi-provider governance and billing |
If your requirement includes both “buy” and “run,” brokerage is the category that ties the chain together.
Integration and Data Flow to Plan
A broker platform sits in the middle of many systems, so integration is not optional. Plan the data flow before you buy.
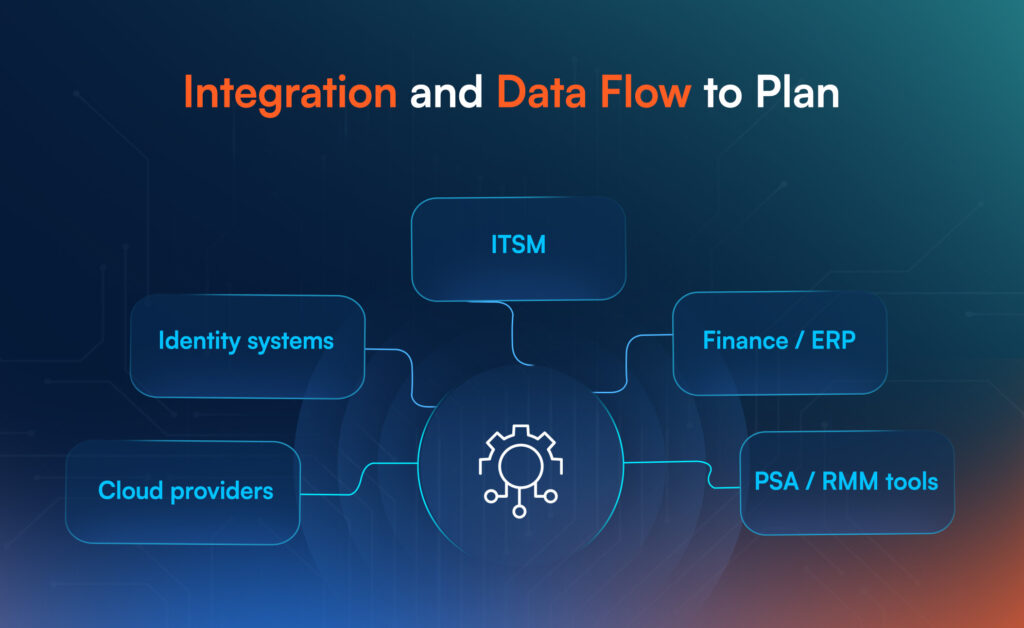
Common integration points
- Cloud providers and marketplaces for catalog, pricing, and provisioning
- Identity providers for access control and logging
- ITSM or ticketing tools for request visibility
- Finance systems for invoicing, taxes, and revenue recognition
- PSA and RMM tools for MSP operations and support
Validate fit by mapping one request path: Request → Approval → Provision → Tag and allocate → Invoice → Renewal. If the platform cannot connect these steps through integrations or exports, work will fall back to spreadsheets and manual reconciliation.
How to Choose Cloud Brokerage Software?
Use this checklist to keep evaluations grounded in operational reality.
| Question | Why it matters | What good looks like |
| Does it support AWS, Azure, GCP, and SaaS listings? | Coverage drives adoption | Connectors plus usable catalog controls |
| Can you enforce approvals and policy gates? | Governance reduces risk | Role-based approvals and audit trails |
| Can finance allocate spend by cost center or product? | Accountability needs structure | Showback or chargeback exports |
| Can it handle subscriptions and usage-based charges? | Billing depth reduces leakage | Rating, proration, taxes, co-terms |
| Can partners sell through a portal? | Channel scale needs tooling | Partner roles, catalogs, deal controls |
| Can it support regional needs in US and India? | Compliance and finance differ | Multi-currency, tax rules, audit exports |
A practical tip: request a sandbox or pilot that includes one full workflow from catalog to invoice. If a vendor cannot demonstrate that chain, the platform will likely create manual work later.
Billing Models a Broker Platform should support
Cloud brokerage is rarely “one price.” A platform becomes easier to run when it supports the billing patterns you actually sell or consume.
| Billing pattern | Where it is common | What the platform must handle |
| Subscription plans | SaaS, managed services, cloud bundles | Recurring invoices, co-terms, add-ons |
| Usage-based charges | Compute, storage, API-based services | Meter ingestion, rating rules, proration |
| Tiered pricing | Volume-based offers | Tier logic and clear invoice breakdown |
| One-time setup fees | Onboarding and migration | One-time line items with approvals |
| Multi-currency and tax rules | Global and India-focused operations | Currency, tax configuration, audit exports |
A rollout plan that avoids common pitfalls
Days 0 to 30: define the catalog and guardrails
Start with 10 to 20 common services. Document:
- Who can request what
- Approval routes
- Budget owners and default tags
- Standard bundles that reduce ad hoc requests
Days 31 to 60: connect provisioning to billing
Link services to billing rules. For MSPs, include subscription plans, add-ons, renewal dates, and metered usage logic where required.
Days 61 to 90: expand coverage and measure adoption
Add more services and teams. Track provisioning time, ticket reduction, billing accuracy, and budget variance. Use those numbers to guide catalog expansion.
How AppGallop Powers Cloud Brokerage And Marketplace Operations?
Cloud brokerage is not only about listing cloud services. It is about running the full operating loop behind them: catalog setup, quoting, provisioning, billing, renewals, and partner delivery. This is where most teams lose time and margin, because the work splits across portals, spreadsheets, ticketing, and manual finance follow-ups. AppGallop helps bring these brokerage workflows into one controlled system so MSPs, resellers, and cloud providers can deliver repeatable outcomes without adding operational load.
1) Turn A Cloud Catalog Into Sellable Offers
AppGallop helps structure cloud products into plans, bundles, and add-ons, so your brokerage is not a raw vendor list. That makes it easier to package value, maintain pricing logic, and keep offers consistent across teams and regions.
2) Run Quote-To-Order And Provisioning As A Workflow
Instead of chasing handoffs, AppGallop supports an ordered flow from request to approval to activation, reducing human dependency for routine fulfillment tasks and keeping delivery consistent across customers.
3) Control Billing, Renewals, And Usage-Based Expansion
Brokerage revenue breaks when billing is delayed, renewals are missed, or usage changes are not captured. AppGallop supports tighter control on subscription lifecycle, renewals, and billing signals, so revenue operations stay clean even as customer count grows.
4) Support Partner-Led Delivery And Multi-Tier Channels
If you sell through channel partners, you need shared visibility without shared chaos. AppGallop supports partner operations through consistent product logic, customer-level control, and standardized processes that work across tiers.
Quick Mapping Table (Keeps The Section Scannable Without Turning It Into Bullets)
| Brokerage Operation Need | What AppGallop Helps You Run | Outcome You Get |
| Offer packaging and catalog control | Plans, bundles, structured offers | Clearer packaging, fewer pricing errors |
| Fulfillment consistency | Quote-to-order workflow + provisioning flow | Fewer manual steps, fewer misses |
| Subscription lifecycle discipline | Renewals, billing control, lifecycle tracking | Cleaner revenue operations |
| Channel execution | Multi-tier partner operations support | Better partner control at scale |
| Governance and reporting | Standardized operational visibility | Faster decisions, fewer surprises |
Conclusion
Cloud brokerage software becomes valuable when multi-cloud starts creating friction across procurement, provisioning, governance, and billing. A strong cloud broker platform turns fragmented services into a governed catalog, applies consistent workflows, and ties every activation to budgets, allocation, and invoicing.
If you are an MSP or reseller, focus on catalog design, bundle logic, and renewal discipline so recurring revenue does not leak through manual steps. If you are an enterprise team, focus on policy guardrails, allocation rules, and audit visibility so usage maps to ownership across clouds.
If you want to see what this looks like in a working workflow, use the CTA above to request a walkthrough of AppGallop’s catalog-to-billing flow.
FAQs
Cloud brokerage software centralizes how you select, manage, and deliver cloud services across providers and customers through one operating layer.
A cloud broker platform runs the operations behind selling and managing cloud services. A marketplace is the storefront, while the broker layer handles catalog logic, fulfillment workflows, billing governance, and ongoing lifecycle control.
Cloud services brokerage adds value on top of cloud services through roles like aggregation, integration, and customization.
Cloud brokerage software supports multi-cloud by keeping cloud services, policies, and operational workflows in one place while still delivering services from different providers. Multi-cloud adoption remains common across organizations.
Cloud brokerage focuses on service delivery, operations, and lifecycle management. CASB focuses on security policy enforcement and visibility for cloud application usage, so the two solve different problems.


